New research confirms that the nation’s blood supply is safe and that blood donations do not need to be screened for COVID-19.

New research confirms that the nation’s blood supply is safe and that blood donations do not need to be screened for COVID-19.
What you need to know
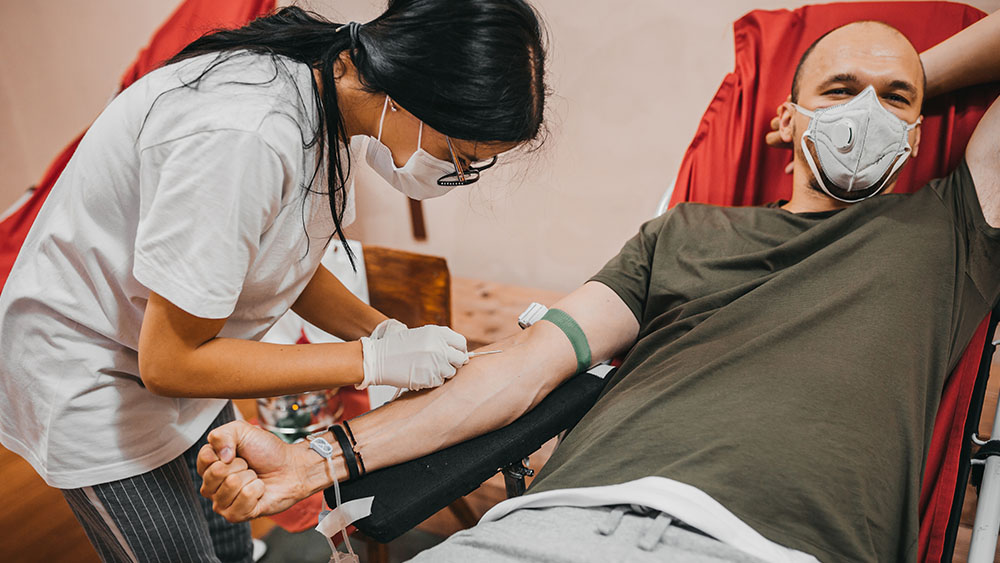
Every year, more than 13 million people in the United States donate to the nation’s blood supply. The blood is given to patients who have lost blood because of surgery or an injury or whose body is not making blood properly.
Blood banks routinely screen blood donors and test donations to make sure that blood transfusions do not transmit disease. Donors are not allowed to donate if they have disease symptoms. In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) reviewed its guidelines for blood safety and recommended that blood banks continue to use the same routine screening measures. Now research from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) validates that recommendation.
What did the researchers do?
Researchers from NHLBI’s Recipient Epidemiology and Donor Evaluation Study (REDS) program tested nearly 18,000 samples of donated blood, from supplies that represented more than 250,000 single blood donations, for the presence of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. The donations were collected between March and September 2020 in six major metropolitan areas. Only three of those samples came back positive for SARS-CoV-2, all with very low amounts of the virus. The likelihood of a patient receiving blood with trace amounts of SARS-CoV-2 is just 0.001% — a little over 1 in 100,000.
In the extremely rare event that a patient would receive blood containing SARS-CoV-2, researchers concluded that the possibility of transmission was insignificant. There have been no reported cases of transfusion-transmitted SARS-CoV-2 — or any other coronavirus — worldwide.
Why is this important?
The nation’s blood supply must be safe. The findings from this research should reassure blood recipients that the blood supply is safe for them and for the people around them. This research should also reassure donors that even if they are asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriers, they cannot spread the virus to blood recipients.
Where can I go to learn more?
U.S. Blood Donations Are Safe Under Current COVID-19 Screening Guidelines
- NHLBI’s press release highlights the safety of the nation’s blood supply.
REDS Epidemiology, Surveillance, and Preparedness of the Novel SARS-CoV-2 Epidemic (RESPONSE)
- The REDS program is evaluating the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in blood donations in the U.S.
- NHLBI explains the blood transfusion process, shares safety information, and presents current research into improved health for blood donors and recipients.
Where to Donate Blood and Convalescent Plasma
- AABB’s blood donation site locator can help you find a location to give blood near you.
Sources
Bakkour, S., Saá, P., Groves, J. A., Montalvo, L., Di Germanio, C., Best, S. M., Grebe, E., Livezey, K., Linnen, J. M., Strauss, D., Kessler, D., Bonn, M., Green, V., Williamson, P., Kleinman, S., Stramer, S. L., Stone, M., & Busch, M. P. (2021). Minipool testing for SARS-CoV-2 RNA in United States blood donors. Transfusion, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/trf.16511

News and Stories
Read stories about the efforts underway to prevent, detect, and treat COVID-19 and its effects on our health.
 An official website of the United States government
An official website of the United States government

